We offer a comprehensive range of prenatal screening.

This screening test combines a blood test with an ultrasound scan to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome. It is performed between 11 and 13 weeks of pregnancy and measures nuchal translucency (fluid at the back of the baby’s neck) and certain pregnancy-related hormones in the mother's blood.

This blood test is performed between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to assess the risk of certain birth defects. It measures four specific substances in the mother's blood: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estriol, and inhibin-A. This screening helps detect conditions such as Down syndrome and neural tube defects.

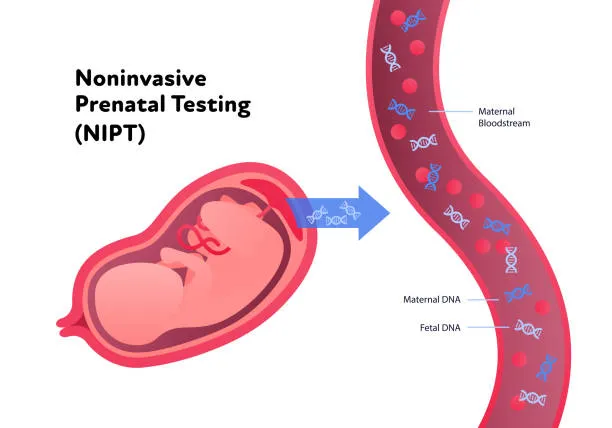
This advanced screening test analyzes fetal DNA circulating in the mother's blood to detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13. It is a safe and highly accurate alternative to invasive diagnostic tests and can be performed as early as 10 weeks into the pregnancy.

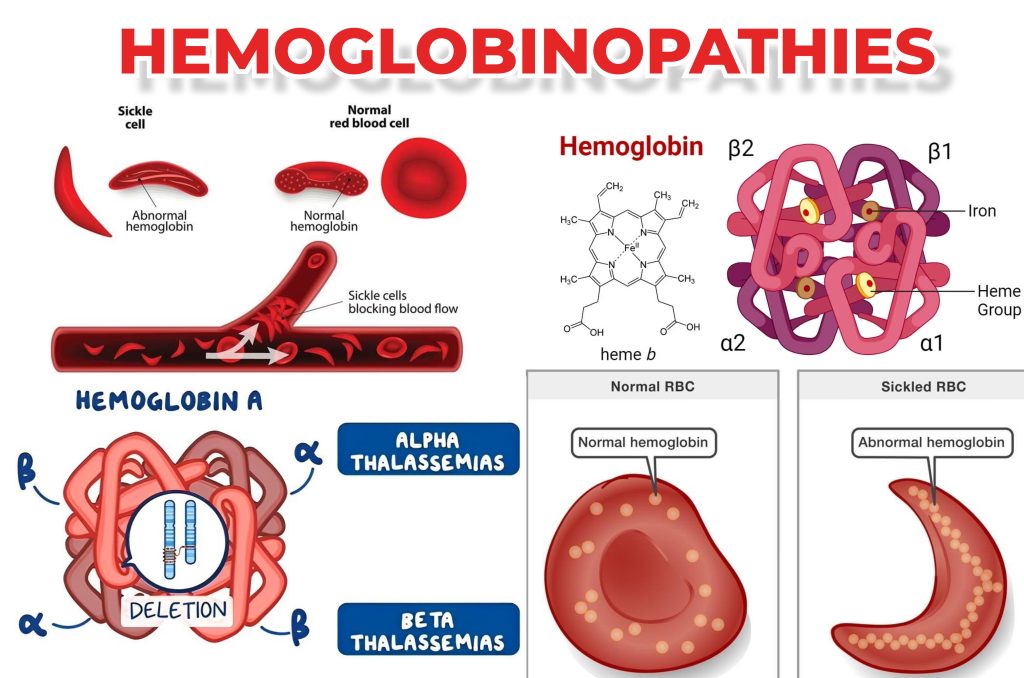
This screening test identifies hemoglobin disorders such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia. It is particularly important for individuals with a family history of these conditions or those belonging to high-risk ethnic groups. Early detection allows for timely management and treatment to ensure the best possible outcomes for the baby.
Prenatal screening refers to tests conducted during pregnancy to assess the health and development of the fetus. These screenings help identify potential genetic disorders, congenital anomalies, and other health conditions early on, allowing for informed decision-making and timely medical intervention.
Considerations and Next Steps
While prenatal screening provides valuable insights, it is important to understand that these tests are not diagnostic. Abnormal results indicate an increased risk but do not confirm a diagnosis. Further diagnostic testing, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, may be recommended for a definitive diagnosis.
Expecting parents should discuss the benefits, risks, and limitations of prenatal screening with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions that align with their values and preferences.